Horizontal directional drilling (HDD), also known as directional boring, is a popular drilling method used in installing underground pipes or cables. It employs the trenchless method instead of digging an open trench. It is particularly helpful in urban areas, environmentally sensitive areas, and areas with existing infrastructure, where traditional excavation methods may be impractical or disruptive. In this article, we will explain the horizontal directional drilling in detail. Let’s start!
What is horizontal directional drilling (HDD)?
Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) is a trenchless drilling method widely used in the installment of underground pipes or cables, unlike traditional open-cut excavation methods. The process of HDD generally involves drilling a pilot hole beneath the ground, enlarging the hole to the required diameter, and placing the pipe in the enlarged hole. It offers an efficient solution for underground utility installations.
Why use HDD?
When the traditional trending method is impractical or not working for some reason, horizontal directional drilling (HDD) is a more practical and effective method. It is particularly invaluable in situations where underground installations need to be carried out horizontally beneath various obstacles such as buildings, roads, rivers, and other existing structures. HDD ensures the integrity and safety of above-ground assets and avoids any interference with the drilling path. This advanced drilling technique has greatly revolutionized underground utility installations.
Advantages of HDD drilling
Compared to old open-cut methods, horizontal directional drilling (HDD) is an advanced technology equipped with many advantages. Here are some of the advantages:
- Less environmental impact
Since HDD requires minimal excavation, it doesn’t bring soil to the ground and stops spreading soil pollution. Thanks to this feature, HDD is beneficial in environmentally sensitive areas, urban settings, or locations with sensitive ecosystems.
- Cost-Effective
HDD costs less than traditional open-cut drilling in almost every way. It needs no extensive restoration and surface repairs. It reduces labor and equipment requirements. It can also save costs associated with traffic management, permits, and mitigating environmental impacts.
- Minimized Disruption
HDD minimizes disruptions to communities and traffic flow. Because the process takes place underground, road closures are not required. Besides, landscaping can be well protected during drilling. Therefore, for installing pipes under areas where interruptions would cause significant inconvenience, HDD is a perfect choice.
- Flexibility
HDD is ideal for installing various sizes and materials of pipes, and types of utilities, such as oil and gas pipelines, water and sewer pipelines, fiber optic cables, telecommunications and electrical conduits, and more. HDD provides greater flexibility than old methods as it can navigate around existing infrastructure, underground utilities, or sensitive areas.
- Longevity
Components of HDD drilling rigs are made from wear-resistant materials, making the equipment more durable. In addition, the seamless, accurate pipe placement reduces the risk of leaks, breaks, or corrosion during operation.
- Efficient Installation
HDD is much more efficient in the installation of pipes or cables compared to conventional methods. It only needs one single bore instead of multiple entry and exit points, leading to significant time and effort savings in excavation and restoration processes. Therefore, HDD is perfect for large-scale projects or those operating under tight deadlines.
How is it done?
HDD is usually conducted and operated by highly trained designers and operators. Their expertise guarantees that the job can be done effectively. Before starting drilling, there is a myriad of tasks waiting for these experts, such as protecting existing utilities and exploring unusual situations underground. The following is the process of the HDD drilling:
- Pilot hole drilling
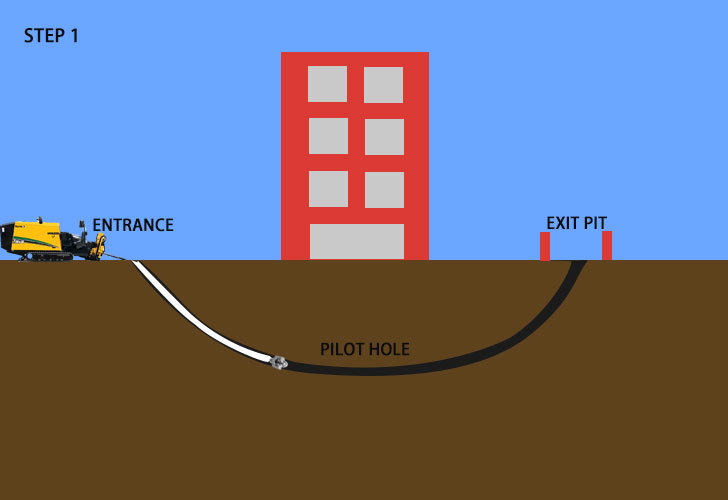
The first task is to drill a pilot hole in a small diameter. Drilling fluid is critical during this process. It is pumped through the drill pipe to the drill bit, and high-pressure jets and the drill bit grind the soil in front of the drill stem. Then, the drilling fluid delivers the cuttings to the entrance pit at the drilling rig. Shots with different sizes employ various ways to track the pilot hole. Larger shots use a wire-line magnetics system, while smaller shots utilize a walkover guidance system. A transmitter or steering tool is employed in both methods. It is placed near the drill head, sending precise coordinates to the engineer, who keeps monitoring the drill head’s data such as depth, alignment, and slope percentage. To ensure the pilot hole remains on the predetermined bore path, The operator constantly makes necessary corrections. The drilling speed is adjusted based on soil conditions and the level of steering required. Once reaching the exit pit, the beacon housing and the drill bit are removed. Then, a reamer is installed.
- Pre-reaming
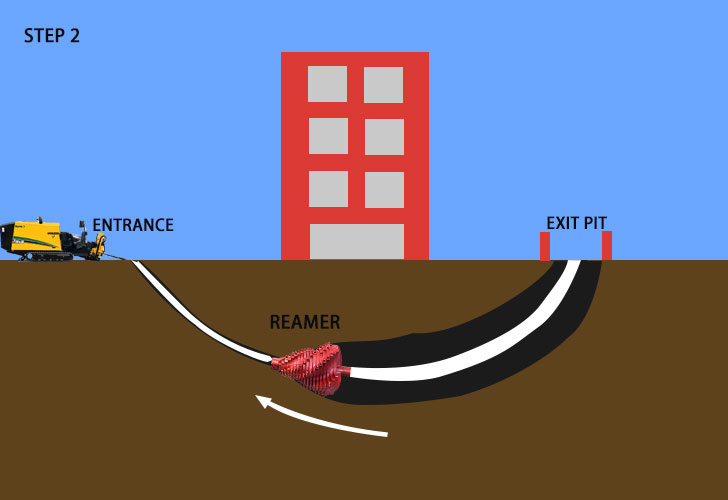
Upon completing the pilot hole, the hole needs to be enlarged to the required diameter for installing the pipeline. This is the second step, called pre-reaming. The pre-reaming is usually done by a reamer. After the drill bit is replaced by a reamer, the reamer is pulled back into the pilot hole created in step one and rotated, meanwhile pumping drilling fluid to cut solids and enlarge the pilot hole. If one pass is not enough to enlarge the hole, it may require a larger reamer and more passes. Soil conditions and the quantity of cuttings can influence the speeds of the reamer. Apart from drilling fluid, Bentonite and polymers are also helpful in creating a clean and stable hole. Bentonite can minimize fluid loss or infiltration and polymers are useful to break up clay soils.
- Pullback operations
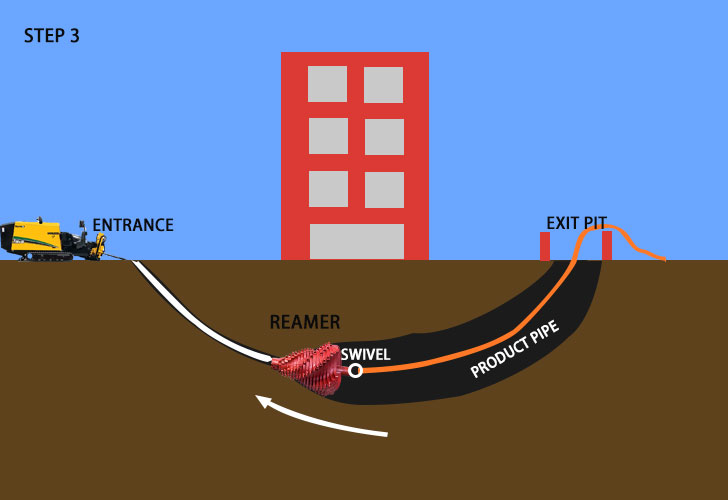
After the pilot hole is pre-reamed, the last step is to pull the conduit back through the hole. A reamer is mounted on the drill stem, and a swivel is employed between the reamer and the prefabricated product pipe. The purpose of using the swivel is to stop the pipe from turning during the drilling process. Then, the HDD rig starts the pullback operation, and drilling fluid is pumped to lubricate the pipe. When the pipeline is in the right place, the pullback operation is finished.
Equipment used in HDD
Different types of horizontal directional drilling rigs are employed in different projects. For demanding crossings, trailer-mounted drills with high performance are needed. Several pieces of ancillary equipment are utilized, including an excavator, high-volume pumps, a drilling fluid reclaimer, and water tanks. When dealing with smaller bores, a range of portable equipment is designed for such applications. Compared to larger bores, the consumption of drilling fluid in drilling smaller bores is greatly reduced. In many cases, fluid is replaced by water, while for even smaller bores, no drilling fluids are necessary.
Tooling
A variety of tooling options are available for HDD drilling. They are tailored to specific purposes and come in various sizes and shapes. In the pilot hole process, a drill bit or roller cone bit is used. For hole enlargement, reamers are employed. Tools designed to deal with challenging formations like hard rock are equipped with tungsten carbide or polycrystalline diamond (PCD) inserts. However, tools for soft soils usually rely on high-carbon steel.
HDD welding teeth/bits
HDD welding teeth or bits are wear parts that are welded on back reamers. They consist of a tungsten carbide tip and a steel body. Tungsten carbide is a type of hard material featuring outstanding hardness and wear resistance. Back reamers with tungsten carbide tips can easily cut hard rocks during operation.
KoneCarbide supplies premium HDD welding teeth/bits. Contact us today if you are looking for a reliable supplier.











